People are excited about Starlink arriving in the North Dundas and North Grenville areas. So what exactly is Starlink? Starlink is a subsidiary of SpaceX, which is the American aerospace company founded in 2002 by Elon Musk. SpaceX began with multiple goals, including reducing earth to orbital launch cost, developing a recoverable launch vehicle, and eventually building a viable vehicle to begin Mars colonisation.
The company has developed a number of high-efficiency, high-performance rocket engines, a number of launch vehicles, cargo and personnel space craft, as well as the the Starlink Satellite Constellation.
A satellite constellation is a series of satellites that communicate with each other. In order to be considered a constellation, there has to be numerous satellites in communication with each other. Many satellites close to each other, that are not in communication with each other, do not constitute a constellation.
Falcon 1 was the first privately-funded launch vehicle to reach orbit on September 28, 2008. The Falcon Heavy was the first privately funded launch vehicle to put a payload into orbit around the sun. That was his Tesla Roadster on February 6, 2018.
SpaceX currently has the lowest cost of earth to low orbit payload insertion in the industry. They are able to put a payload into orbit for $28 million, charging their clients approximately $62 million for the service. SpaceX currently performs two thirds of NASA’s launches, and won a contract in 2020 for 40% of the US Space Force launches through to 2027.
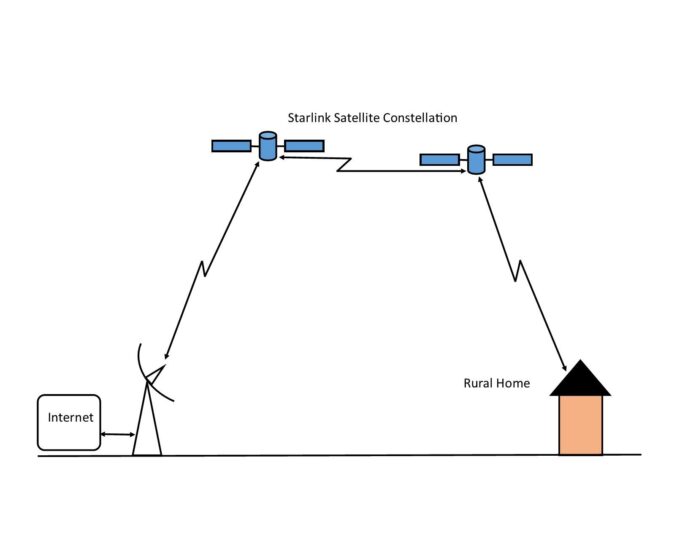
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation constructed by SpaceX. Upon completion, it will include thousands of small mass-produced communication satellites in low earth orbit (LEO) working in conjunction with multiple ground stations. The company promises high-speed, low latency, broadband internet to users worldwide, especially those in rural or remote locations. They advertise 50 to 150 Mbps, depending on location.
The company is now selling beta service internationally in several locations with global coverage advertised by the end of 2021. Beta is a testing phase, prior to official release. The company claims that the service is ideal for rural and remote communities where traditional landline infrastructure would be prohibitively expensive. Current service is $799 Canadian up front for equipment cost, and $129 Canadian per month for 50 to 150 Mbps unlimited data. Availability is currently limited, with potential periodic outages to be expected during the beta phase.
Starlink works as such: There is a network server farm, connected by a fibre backbone to a satellite ground station. This satellite ground station transmits to, and receives from, a satellite in the constellation, which itself transmits to, and receives from, other satellites in the constellation. Each of the satellites then transmit to, and receive from, a large footprint (area) on the earth. Any Starlink transceiver within that footprint (area) is able to transmit to, and receive from, that satellite. The end goal is to create a web of communications satellites enabling internet access from anywhere in the world.
Elon Musk aims to have 11,943 satellites circling the earth by 2025, with an end goal of 42,000. Light pollution is already a large concern for astronomers. Many astronomical images taken over the last year have been near useless because of trails of light across them.